 |
 |
 |
 |
The Most Comprehensive Stool Tests for Optimal Clinical Utility
The GI Effects® Comprehensive Stool Profile
is a group of advanced stool tests that provide immediate, actionable
clinical information for the management of gastrointestinal health.
Utilizing cutting-edge technologies and biomarkers, this profile offers
valuable insight into digestive function, intestinal inflammation, and
the intestinal microbiome.
GI Effects Gets a Makeover
Genova Diagnostics is excited to announce an added level of
enhanced clinical utility to GI Effects reporting. New enhancements make
interpretation quicker and easier to prioritize treatment and assess
microbiome status.
The report will now synthesize findings by integrating a novel, proprietary scoring system. These Functional Imbalance Scores
will help direct targeted therapeutic recommendations with support
options included on the front page of the report. Clinicians can
prioritize test findings and treatment based on score severity and can
track scores over time. Biomarkers are grouped and scored in 5 key areas
relating to GI function:
- Maldigestion
- Inflammation
- Dysbiosis
- Metabolite Imbalance
- Infection
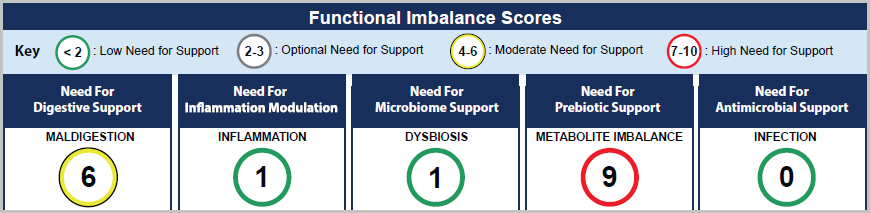
Genova is the first laboratory to introduce an
Inflammation-Associated Dysbiosis score and a Methane Dysbiosis score by
incorporating our latest, published microbiome data analysis.1
These new patterns of dysbiosis can help differentiate treatment
interventions. Additionally, we provide new graphics to better
understand commensal bacteria patterns. Information about the patient's
microbiome is organized into 3 areas:
- Abundance
- Dysbiosis
- Balance
We invite you to download the GI Effects Sample Report and listen to the The Lab Report Podcast episode introducing you to the new, improved report!
The Genova Difference
Why Choose Genova Diagnostics' Gastrointestinal Products?
- GI Effects is a comprehensive assessment of complete gut health, assessing the root cause of most GI complaints.
- Genova uses a combination of PCR, culture, and microscopic methods to ensure any and all relevant organisms are identified.
- Genova recovers live organisms (yeast and bacteria) for susceptibility testing and improved treatment options.
- Genova measures metabolomics and can assess the interaction between the microbiome and its host.
- Genova is the market authority on stool inflammatory markers, testing calprotectin, EPX and sIgA.
- Genova has amassed a database of hundreds of thousands of complete stool profiles. Our data driven and evidence-based analysis ensures the highest standard of analytical validity and clinical utility.
Learn more about Genova's Comprehensive GI Testing Value.
Clinical Overview
When Should the GI Effects Comprehensive Stool Profile Be Considered?
The GI Effects Comprehensive Stool Profile can reveal important
information about the root cause of many common gastrointestinal
symptoms such as gas, bloating, indigestion, abdominal pain, diarrhea,
and constipation. This stool analysis utilizes biomarkers such as fecal
calprotectin to differentiate between Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
and Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS).4,5
In addition, Genova's GI Effects test can be used to evaluate patients
with a clinical history that suggests a gastrointestinal infection or
dysbiosis.
Gut microbes are codependent with one another and with their human
host, and the health of one affects the other. A sizeable volume of
research associates a dysbiotic, or imbalanced gut microbiome with
multiple disease states both within and outside of the GI tract.2,3
The diverse metabolic activities of the microbiome ultimately impact
the human host, and the activities of the human host ultimately affect
the health of their microbiome.
The GI Effects Comprehensive Stool Profile Biomarkers
The biomarkers on the GI Effects Comprehensive Profile reflect the 3 key functions of gut health arranged in the "DIG" format: Digestion/Absorption, Inflammation/Immunology, and the Gut Microbiome:
- Digestion/Absorption:
- Pancreatic Elastase-1 is a marker of exocrine pancreatic function.
- Products of Protein Breakdown are markers of undigested protein reaching the colon.
- Fecal Fat is a marker of fat breakdown and absorption.
- Inflammation/Immunology:
- Calprotectin is a marker of neutrophil-driven
inflammation. Produced in abundance at sites of inflammation, this
biomarker has been proven clinically useful in differentiating between
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) and Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS).4,5
- Eosinophil Protein X is a marker of eosinophil-driven inflammation and allergic response.
- Fecal Secretory IgA is a marker of gut secretory immunity and barrier function.
- Fecal Occult Blood Test detects hidden blood; fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) has been recommended by the American College of Gastroenterology as the preferred noninvasive test for colorectal cancer screening/detection.
- Gut Microbiome:
- Metabolic indicators, including short-chain fatty
acids and beta-glucuronidase, demonstrate specific and vital metabolic
functions performed by the microbiota.
- Commensal Bacteria demonstrate the composition and relative abundance of gut organisms.
- More than 95% of commensal gut organisms are anaerobic and are difficult to recover by traditional (aerobic) culture techniques.
- GI Effects assesses a set of 24 genera/species that map to 7 major phyla.
- Bacterial and mycology cultures demonstrate the presence of specific beneficial and pathological organisms.
- Bacterial and mycology sensitivities are provided
for pathogenic or potentially pathogenic organisms that have been
cultured. The report includes effective prescriptive and natural agents.
- Parasitology includes comprehensive testing for all parasites on every parasitology exam ordered.
- GI Effects provides microscopic fecal specimen examination for ova and parasites (O&P), the gold standard of diagnosis for many parasites.
- 6 Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) targets detect common protozoan parasites including Blastocystis spp. with reflex subtyping 1-9, Cryptosporidium parvum/hominis, Cyclospora cayetanensis, Dientamoeba fragilis, Entamoeba histolytica, and Giardia. PCR for organisms is emerging as a highly sensitive method for infectious organism detection.
- Selection of a one-day or three-day sample collection is based on
the clinician's clinical index of suspicion for parasitic infection. If
there is no/low suspicion, a one-day sample will likely be adequate.
For high suspicion, a three-day sample collection is optimal.
- Additional Biomarkers Available:
- Campylobacter
- Clostridium difficile
- Escherichia coli
- Fecal Lactoferrin
- Helicobacter pylori
- Macro Exam for Worms
- Zonulin Family Peptide
- KOH Preparation for Yeast
What Advantage Does the Profile Offer Compared to Other Diagnostics?
A structured fecal biomarker panel offers the advantage of assessing
multiple functional areas that may be contributing to symptoms. For
example, diarrhea could stem from multiple causes including pancreatic
exocrine insufficiency, inflammation, food allergies, or the presence of
a pathogenic or potentially pathogenic organism. A positive result on
one or more fecal biomarker tests may guide therapy, either by
suggesting a treatable alternative diagnosis or by eliminating a
diagnosis from further consideration. The latter allows individualized
targeted treatment to be redirected to more likely diagnoses.6,7
GI Effects® represents the best technical platform available to assess the gut microbiome, combining:
- 16S rRNA gene polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification technique for anaerobic commensal bacteria
- Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass
Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) technology for limitless bacterial and
fungal species identification via culture
- Gold standard microscopic ova and parasite (O&P) detection
- Real-time PCR for the identification of 6 common parasites
- Next-Generation DNA sequencing for Blastocystis spp. with reflex subtyping 1-9
The test report findings are synthesized into a results overview
that helps the clinician to prioritize findings with functional
imbalance scores and therapeutic support options. Furthermore, Genova
summarizes the status of the patient's commensal bacteria levels with
clinically actionable data.
What Can Clinicians and Patients Expect from GI Effects Comprehensive Profile Stool Testing?
The GI Effects Stool Profile biomarkers provide comprehensive
information for the development of strategic interventions. Symptoms
often improve as identified functional imbalances and inadequacies
become normalized through targeted dietary, lifestyle, and
supplementation therapeutics.
References
- Chen
L, et. al. Development of an Index Score for Intestinal
Inflammation-Associated Dysbiosis Using Real-World Stool Test Results. Dig Dis Sci. 2019.
- Marchesi J, et. al. The gut microbiota and host health: a new clinical frontier. Gut. 2016 Feb;65(2):330-9.
- Clemente J, et. al. The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: an integrative review. Cell. 2012 Mar;148(6):1258-70.
- Menees
SB, et. al. A meta-analysis of the utility of C-reactive protein,
erythrocyte sedimentation rate, fecal calprotectin, and fecal
lactoferrin to exclude inflammatory bowel disease in adults with IBS. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015 Mar;110(3):444-54.
- Dabritz J, Musci J, Foell D. Diagnostic utility of faecal biomarkers in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jan;20(2):363-375.
- Parsons K, et. al. Novel testing enhances irritable bowel syndrome medical management: the IMMINENT study. Glob Adv Health Med. 2014 May;3(3):25-32.
- Goepp J, et. al. Frequency of abnormal fecal biomarkers in irritable bowel syndrome. Glob Adv Health Med. 2014 May;3(3):9-15.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |

|